Photography is an expansive art form that includes more than just portraiture, landscape or glamour photography. Both professional and amateur photographers may favor specific types of photography over others. While a professional photographer may work in photojournalism, an amateur may be particularly interested in macrophotography. Read on to learn more about the various types of photography.
Photojournalism

Although amateurs may break into this field without formal training, photojournalism is often limited to professionals. One reason photojournalism is generally practiced by professionals is that serious photojournalists must be sure that their shots maintain the integrity of the original scene. Photojournalism requires the photographer to shoot only the facts: no alteration or embellishment of the photo is permitted. Photojournalism pictures are often powerful images that engage the viewer with the news story. Knowing how to take such shots to capture the original emotion is often learned only through years of practice and experience.
Photo journalism is a particular form of journalism (the collecting, editing, and presenting of news material for publication or broadcast) that creates images in order to tell a news story. It is now usually understood to refer only to still images, but in some cases the term also refers to video used in broadcast journalism. Photojournalism is distinguished from other close branches of photography (e.g., documentary photography, social documentary photography, street photography or celebrity photography) by complying with a rigid ethical framework which demands that the work is both honest and impartial whilst telling the story in strictly journalistic terms. Photojournalists create pictures that contribute to the news media.
Timeliness — the images have meaning in the context of a recently published record of events.
Objectivity — the situation implied by the images is a fair and accurate representation of the events they depict in both content and tone.
Narrative — the images combine with other news elements to make facts relatable to the viewer or reader on a cultural level.
Like a writer, a photojournalist is a reporter but he or she must often make decisions instantly and carry photographic equipment, often while exposed to significant obstacles (e.g., physical danger, weather, crowds).
Photo journalism is a particular form of journalism (the collecting, editing, and presenting of news material for publication or broadcast) that creates images in order to tell a news story. It is now usually understood to refer only to still images, but in some cases the term also refers to video used in broadcast journalism. Photojournalism is distinguished from other close branches of photography (e.g., documentary photography, social documentary photography, street photography or celebrity photography) by complying with a rigid ethical framework which demands that the work is both honest and impartial whilst telling the story in strictly journalistic terms. Photojournalists create pictures that contribute to the news media.
Timeliness — the images have meaning in the context of a recently published record of events.
Objectivity — the situation implied by the images is a fair and accurate representation of the events they depict in both content and tone.
Narrative — the images combine with other news elements to make facts relatable to the viewer or reader on a cultural level.
Like a writer, a photojournalist is a reporter but he or she must often make decisions instantly and carry photographic equipment, often while exposed to significant obstacles (e.g., physical danger, weather, crowds).
Documentary Photography

Documentary photographs tell stories with images. The main difference between photojournalism and documentary photography is that documentary photography is meant to serve as a historical document of a political or social era while photojournalism documents a particular scene or instance. A documentary photographer may shoot a series of images of the inner city homeless or chronicle the events of international combat. Any topic may be the subject of documentary photography. As with photojournalism, documentary photography seeks to show the truth without manipulating the image.
Documentary photography usually refers to a popular form of photography used to chronicle significant and historical events. It is typically covered in professional photojournalism, or real life reportage, but it may also be an amateur, artistic, or academic pursuit. The photographer attempts to produce truthful, objective, and usually candid photography of a particular subject, most often pictures of people.
Documentary photography usually refers to a popular form of photography used to chronicle significant and historical events. It is typically covered in professional photojournalism, or real life reportage, but it may also be an amateur, artistic, or academic pursuit. The photographer attempts to produce truthful, objective, and usually candid photography of a particular subject, most often pictures of people.
Action Photography

While professionals who take action shots may specialize in a variety of different subjects, sports photography is one of the fastest and most exciting types of photography. As with any action shot, a good sports photographer has to know his or her subject well enough to anticipate when to take pictures. The same rule goes for photographers taking action shots of animals in nature or of a plane taking off.
The main application of professional sports photography is for editorial purposes; dedicated sports photographers usually work for newspapers, major wire agencies or dedicated sports magazines. However, sports photography is also used for advertising purposes both to build a brand and as well as to promote a sport in a way that cannot be accomplished by editorial means
The main application of professional sports photography is for editorial purposes; dedicated sports photographers usually work for newspapers, major wire agencies or dedicated sports magazines. However, sports photography is also used for advertising purposes both to build a brand and as well as to promote a sport in a way that cannot be accomplished by editorial means
Macro Photography

Macrophotography describes the field of photography in which pictures are taken at close range. Once restricted to photographers with advanced and expensive equipment, macrophotography is now easier for amateurs to practice with digital cameras with macro settings. Macrophotography subjects may include insects, flowers, the texture of a woven sweater or any object where close-up photography reveals interesting details.Macro photography (or photomacrography or macrography, and sometimes macrophotography is extreme close-up photography, usually of very small subjects, in which the size of the subject in the photograph is greater than life size (though macrophotography technically refers to the art of making very large photographs). By some definitions, a macro photograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative or image sensor is life size or greater. However in other uses it refers to a finished photograph of a subject at greater than life size.
The ratio of the subject size on the film plane (or sensor plane) to the actual subject size is known as the reproduction ratio. Likewise, a macro lens is classically a lens capable of reproduction ratios greater than 1:1, although it often refers to any lens with a large reproduction ratio, despite rarely exceeding
The ratio of the subject size on the film plane (or sensor plane) to the actual subject size is known as the reproduction ratio. Likewise, a macro lens is classically a lens capable of reproduction ratios greater than 1:1, although it often refers to any lens with a large reproduction ratio, despite rarely exceeding
Microphotography
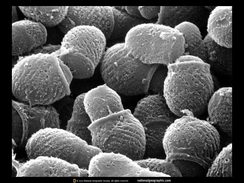
Microphotography uses specialized cameras and microscopes to capture images of extremely small subjects. Most applications of microphotography are best suited for the scientific world. For example, microphotography is used in disciplines as diverse as astronomy, biology and medicine.Microphotographs are photographs shrunk to microscopic scale (see microfilm) – not to be confused with photomicrographs, which are photographs of microscopic things.Microphotography is the art of making such images.
Using the daguerreotype process, John Benjamin Dancer was one of the first to produce microphotographs, in 1839. He achieved a reduction ratio of 160:1. Dancer perfected his reduction procedures with Frederick Scott Archer’s wet collodion process, developed in 1850–51, but he dismissed his decades-long work on microphotographs as a personal hobby, and did not document his procedures. The idea that microphotography could be no more than a novelty was an opinion shared by the 1858 Dictionary of Photography, which called the process "somewhat trifling and childish.
Novelty viewing devices such as Stanhopes were once a popular way to carry and view microphotographs.
An important application of microphotography is in microforms.
Using the daguerreotype process, John Benjamin Dancer was one of the first to produce microphotographs, in 1839. He achieved a reduction ratio of 160:1. Dancer perfected his reduction procedures with Frederick Scott Archer’s wet collodion process, developed in 1850–51, but he dismissed his decades-long work on microphotographs as a personal hobby, and did not document his procedures. The idea that microphotography could be no more than a novelty was an opinion shared by the 1858 Dictionary of Photography, which called the process "somewhat trifling and childish.
Novelty viewing devices such as Stanhopes were once a popular way to carry and view microphotographs.
An important application of microphotography is in microforms.
Glamour Photography

Glamour photography, sometimes confused with pornography, may be sexy and erotic but it is not pornographic. Instead of focusing on nudity or lurid poses, glamour photography seeks to capture its subject in suggestive poses that emphasize curves and shadows. As the name implies, the goal of glamour photography is to depict the model in a glamorous light. Consequently, many glamour shots carry flirtatious, mysterious and playful tones.
Portraiture

Portraiture is one of the oldest types of photography. Whether the subject is your family or your pet, the goal of portraiture is to capture the personality of the subject or group of subjects on film.
Portraiture may refer to:
The creation of any portrait, an artistic representation of a person, including
Portrait painting
Portrait photography
Self-portrait
Portraiture may refer to:
The creation of any portrait, an artistic representation of a person, including
Portrait painting
Portrait photography
Self-portrait
Underwater Photography

Underwater photography is usually employed by scuba divers or snorkelers. However, the cost of scuba diving, coupled with often expensive and unwieldy underwater photography equipment, makes this one of the less common types of photography. Similarly, if an amateur has the equipment and the scuba know-how, taking shots underwater can be complicated, as scuba goggles are magnified and distort the photographer’s vision.Underwater photography is the process of taking photographs while under water. It is usually done while scuba diving, but can be done while snorkeling or swimming.
Successful underwater imaging is usually done with specialized equipment and techniques. However, it offers exciting and rare photographic opportunities. Animals such as fish and marine mammals are common subjects, but photographers also pursue shipwrecks, submerged cave systems, underwater "landscapes", and portraits of fellow divers.
Since underwater photography is often performed while scuba diving, it is important that the diver-photographer be sufficiently skilled so that it remains a reasonably safe activity. Good scuba technique also has an impact on the quality of images, since marine life is less likely to be scared away by a calm diver, and the environment is less likely to be damaged or disturbed. There is the possibility of encountering poor conditions, such as heavy currents, tidal flow, or poor visibility. Underwater photographers usually try to avoid these situations whenever possible. Underwater diving training providers such as the Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI) provides courses to help improve a divers diving skills and underwater photography skills.
Successful underwater imaging is usually done with specialized equipment and techniques. However, it offers exciting and rare photographic opportunities. Animals such as fish and marine mammals are common subjects, but photographers also pursue shipwrecks, submerged cave systems, underwater "landscapes", and portraits of fellow divers.
Since underwater photography is often performed while scuba diving, it is important that the diver-photographer be sufficiently skilled so that it remains a reasonably safe activity. Good scuba technique also has an impact on the quality of images, since marine life is less likely to be scared away by a calm diver, and the environment is less likely to be damaged or disturbed. There is the possibility of encountering poor conditions, such as heavy currents, tidal flow, or poor visibility. Underwater photographers usually try to avoid these situations whenever possible. Underwater diving training providers such as the Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI) provides courses to help improve a divers diving skills and underwater photography skills.
Travel Photography

Travel photography may span several categories of photography, including advertising, documentary or vernacular photography that depicts a particularly local or historical flavor. A travel photographer can capture the feel of a location with both landscapes and portraiture.Travel photography is a subcategory of photography involving the documentation of an area's landscape, people, cultures, customs and history. The Photographic Society of America defines a travel photo as an image that expresses the feeling of a time and place, portrays a land, its people, or a culture in its natural state, and has no geographical limitations.
Travel photography can either be created by professionals or amateurs. Examples of professional travel photography can be found in the National Geographic magazine. Amateur travel photography is often shared online through photo sharing websites like Flickr or niche travel photography websites such as TrekEarth.
Travel photography can either be created by professionals or amateurs. Examples of professional travel photography can be found in the National Geographic magazine. Amateur travel photography is often shared online through photo sharing websites like Flickr or niche travel photography websites such as TrekEarth.
Wedding Photography

Wedding photography is a blend of different types of photography. Although the wedding album is a documentary of the wedding day, wedding photos can be retouched and edited to produce a variety of effects. For example, a photographer may treat some of the pictures with sepia toning to give them a more classic, timeless look. In addition, a wedding photographer must have portrait photography skills. He may also have to employ glamour photography techniques to capture the bride and groom at their best.
Advertising Photography

Because photography plays a vital role in advertising, many professional photographers devote their careers to advertising photography. The need for unique and eye-catching advertising copy means the photographer may work with multiple types of photography, including macrophotography and glamour photography.
Art Photography

Artistic photography can embrace a wide variety of subjects. While a nature photographer may use underwater photography to create an art show based on sea life, a portrait photographer’s show may feature black and white artistic portraitures. In all cases, the photographs must have aesthetic value to be considered art. Art photography is photography created in accordance with the vision of the artist as photographer. Fine art photography stands in contrast to photojournalism, which provides a visual account for news events, and commercial photography, the primary focus of which is to advertise products or services.
Aerial Photography

An aerial photographer specializes in taking photos from the air. Photos may be used for surveying or construction, to capture birds or weather on film or for military purposes. Aerial photographers have used planes, ultralights, parachutes, balloons and remote controlled aircraft to take pictures from the air.Aerial photography is the taking of photographs of the ground from an elevated position. The term usually refers to images in which the camera is not supported by a ground-based structure. Cameras may be hand held or mounted, and photographs may be taken by a photographer, triggered remotely or triggered automatically. Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, multirotor Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), balloons, blimps and dirigibles, rockets, kites, poles, parachutes, and vehicle mounted poles. Aerial photography should not be confused with Air-to-Air Photography, when aircraft serve both as a photo platform and subject.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed